
Once considered to be science fiction and fodder for Hollywood films, artificial intelligence (AI) has become a near-ubiquitous technology in our communities, homes and workplaces that is helping to improve our day-to-day lives. The groundwork is now being laid for a more AI-enabled future – one where creativity can be enhanced, productivity can be increased, and business can operate more reliably and efficiently.
What is artificial intelligence?
Artificial intelligence is a term applied to computers, robots, or machines that exhibit aspects of human intelligence and reasoning, such as visual perception, speech recognition, and decision-making.
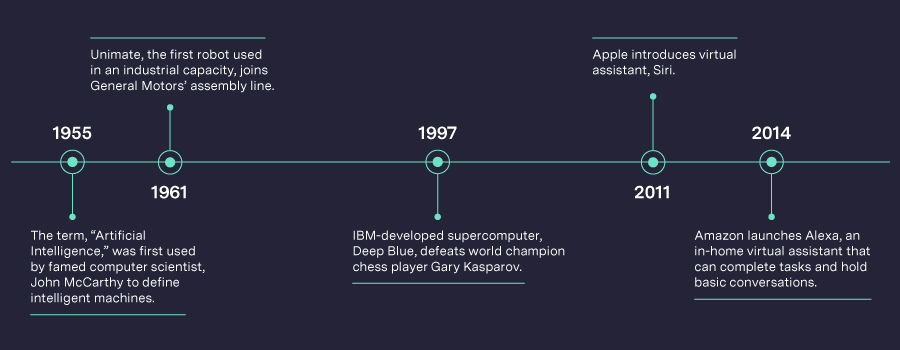
Brief timeline of milestones in AI development:
To achieve these capabilities, AI works by processing data to identify patterns, make predictions, and recommend actions on any given task. AI is commonly broken into two categories:
- Weak AI – otherwise known as ‘narrow AI’ – is focuses on performing a specific task or function, and generally requires human interfacing to operate. Examples of weak AI include Apple’s Siri, Amazon’s Alexa, or Google Assistant. These virtual assistants can understand certain keywords and produce responses to commands but can’t discern the meaning of what was said.
- Strong AI – In contrast, strong AI is general in its function and it can reason, plan, learn and problem-solve autonomously. Currently, strong AI is theoretical and there are no practical examples of it in use today, but numerous applications are in development. One area that strong AI could be applied is cybersecurity, where AI intelligence could aid in breach detection, threat intelligence and risk analysis.
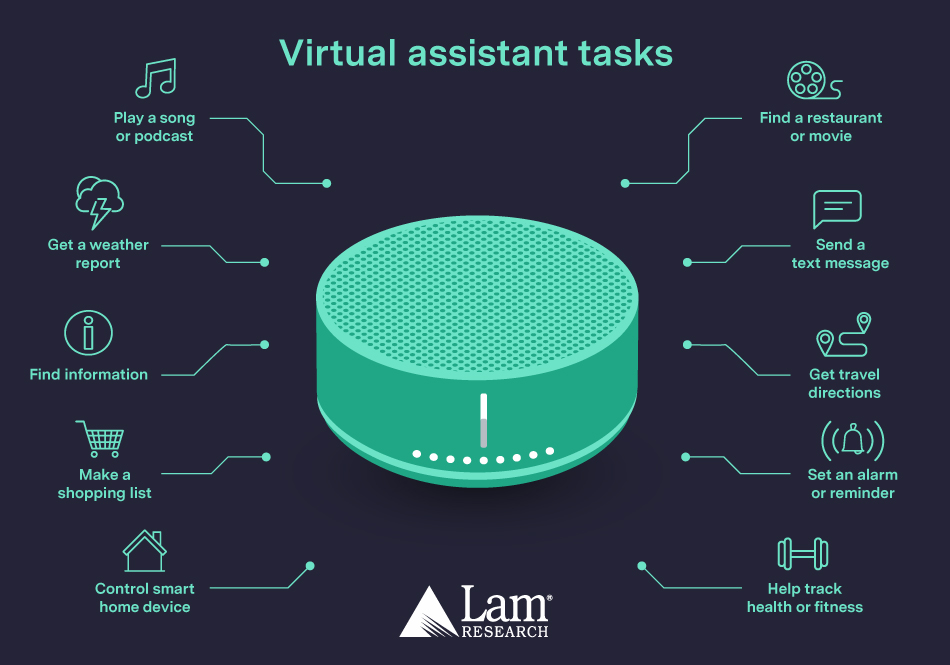
Subsets of artificial intelligence
Machine learning and deep learning are subcategories of artificial intelligence. While AI is a term to describe intelligent machines that can reason and perform tasks autonomously, machine learning refers to a type of AI that enables software applications that leverage algorithms and historical data to learn over time and predict likely outcomes. Another AI subtype is deep learning, which uses neural networks that imitate the human brain’s ability to analyze data and learn by identifying patterns in a given dataset.
A key differentiator between deep learning and machine learning is how the systems learn and are trained. For example, if you were to sort your photos in your phone, you would need to present the machine learning algorithm with structured data: data that is categorized with identifiers, for instance like a digital photo album of pets, or landscapes, or family members. Once fed through the system, the machine learning algorithm will sort based on what it has learned from your tagged photos. Deep learning on the other hand doesn’t require structured data to categorize your images. Instead, it processes the image through neural networks that enable it to classify specific features. In other words: if a photo contains a mountain or a body of water, the algorithm will classify it as a landscape and if the photo has fur and whiskers, the system can identify it as a type of animal, like a dog or a cat.
The analysis of visual information is an exciting field within artificial intelligence. Called computer vision, the technology goes beyond image processing to identifying and interpreting the data contained in the image, then applying that knowledge. For example, facial recognition is a type of computer vision that not only perceives facial features, but can go further and identify the face as being the phone’s owner.
Applications of artificial intelligence
Let’s take a quick look at some other examples of how artificial intelligence is enhancing our lives.
 |
Applications like Google Translate can be used to transcribe spoken words into written text with automatic speech recognition. The application is also able to understand and translate spoken words. |
 |
Natural language processing has reshaped the modern workplace. With AI-powered applications like chatbots and voice assistants, businesses can interact with their customers in real-time, regardless of the time of day. Additionally, spelling auto-correct and email filters enable employees to send more polished, -error-free responses to customers and clients. |
 |
In the construction industry, AI is helping to make construction sites safer and more secure. Using computer vision, another subset of AI, to analyze video data in real-time to monitor and detect unsafe conditions or faulty machinery and help predict when accidents or equipment failures are likely to occur. |
 |
Home security has been drastically improved by the introduction of AI-powered smart home applications. These smart monitoring systems have helped to reduce the number of thefts and break-ins with smart cameras that incorporate AI and facial recognition capabilities. |
Specialized chips
Ultimately, AI is reliant on microchips, which support the cognitive functions of AI-enabled applications that are compute and memory-intensive. The continued evolution of semiconductors has enabled AI to become part of our everyday devices.
The recent advancements in specialized chips have enabled the development of embedded AI: instead of AI computation and processing occurring in the cloud, AI functions can now be performed at the device-level.
AI’s evolving impact on our world has never been more evident, as this once nascent technology now resides in our smartphones and other devices, and it continues to improve the functionality and efficiency of our lives. From auto-correcting our spelling and grammar, to securing physical constructions sites and our digital identities and assets online, AI’s transformative impact can be seen and felt just about everywhere.
Curious to understand how Lam Research is using AI in its tools and services? Watch this space to learn more in future posts!